West nile virus encephalitis pdf
West Nile virus encephalitis (WNE) is the most common neuroinvasive manifestation of WNND. WNE presents with similar symptoms to other viral encephalitis with …
To the Editor: In a letter to the editor, Krishnamoorthy et al. question the diagnosis of “acute West Nile encephalitis” in our case report. We did not use the word “acute” in the paper, but the patient did in fact have an acute illness. We believe that this case report, in which West Nile
West Nile Virus • First identified in 1937 in the West Nile Province of Uganda in the blood of a febrile woman • Known at first as a cause of a febrile fever
Our patient had encephalitis associated with West Nile virus infection, although other viral infections can produce similar symptoms. Testing of both blood and cerebrospinal fluid is necessary to pinpoint the infectious source. A flavivirus, West Nile is one of the most widespread arboviruses in the world. Mosquitos belonging to the genus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a small RNA virus. It was first isolated in the blood of a febrile woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937. Although WNV has caused human disease in Africa and Europe since its identification, the first documented human infections occurred in the United States in
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause mild illness (West Nile fever) or severe symptoms (encephalitis or meningitis – inflammation of the brain) in humans and other animals. People primarily get West Nile from the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds that carry the virus in their blood.
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (80.0 KB) Introduction. Recent epidemiological investigations have implicated blood products and donated organs as sources of infection with the West Nile virus (WNV) . The clinical course appears to be particularly severe in organ recipients on immunosuppressive drugs and has led to
West Nile Virus Meningoencephalitis: MR Imaging Findings Kalliopi A. Petropoulou, Steven M. Gordon, Richard A. Prayson, and Paul M. Ruggierri BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Reports of MR imaging in West Nile virus (WNV) menin-goencephalomyelitis are few and the described findings limited. The purpose of this study was to review the spectrum of MR imaging findings for WNV …
West Nile Virus. West Nile virus (WNV) is an important cause of arboviral infections of the central nervous system (CNS) in the U.S.123 The combined presence of acute encephalitis with multifocal chorioretinitis and vitritis should prompt consideration of WNV or other arbovirus infections.
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Romina Deldar , Derek Thomas , and Anna Maria Storniolo Division of Hematology & Oncology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202, USA
West Nile Encephalitis Publications PubFacts

West Nile virus epidemiology and factors triggering change
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of West Nile virus infection Lyle R Petersen, MD, MPH INTRODUCTION — West Nile (WN) virus, a flavivirus that is a member of the Japanese encephalitis virus antigenic complex, emerged from obscurity in 1999 when the first incursion of the virus in North America caused 62 cases of encephalitis and seven deaths in New York [1]. Since that time, the virus …
West Nile virus (WNV) is found throughout Africa, Europe, Central Asia, and, most recently, in North America. The first outbreak in the United States was in New York City during the summer of 1999, and the virus subsequently spread across the United States ( 1 ).
West Nile Virus (WNV) is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae. Outbreaks West Nile Virus (WNV) was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
Photomicrograph of West Nile virus encephalitis showing perivascular lymphocytic cuffing (lower right), microglial influx and clusters (upper left), and loss of pigmented neurons in the substantia nigra (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×200).
colon; West Nile virus (WNV) has recently emerged as a significant and increasingly frequent etiology of encephalitis in this country. Even though WNV has been in the limelight of the national news media and in the public arena, recognition of WNV encephalitis is frequently not overtly apparent.
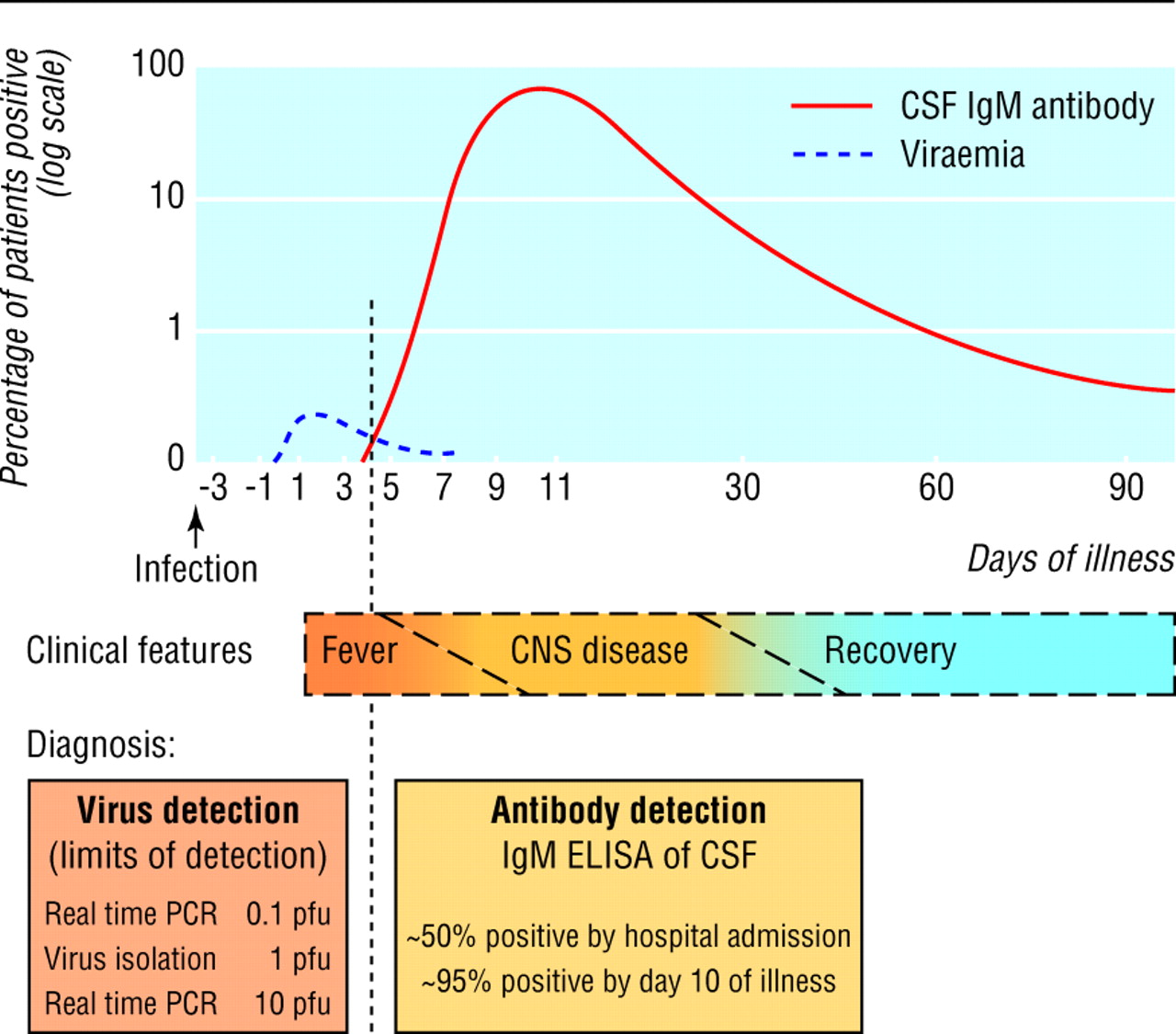
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus transmitted in natural cycles between birds and mosquitoes, particularly Culex spp. (Fig. 1) (104), and was first isolated in
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
agency, but whose blood tested positive when screened for the presence of West Nile virus or Zika virus. Unless they meet the case Unless they meet the case reporting criteria, they are not counted as a case for official reporting purposes and are not included in the “Total” column.
Abstract. West Nile virus infection has become the predominant cause of flavivirus-associated encephalitis in the US. While 80 % of infected individuals are asymptomatic, 20 % develop symptoms including fever, headache, transient rash and gastrointestinal symptoms.
West Nile fever is a zoonotic disease (an animal disease affecting humans). Disease is caused by West Nile virus (WNV), which is a flavivirus related to the viruses that cause St. Louis encephalitis, Japanese encephalitis, and yellow fever.
West Nile virus (WNV) is an emerging pathogen whose ecology and epidemiology extend across multiple interfaces including the viral pathogen, arthropod vectors, …
Japanese encephalitis and West Nile viruses are members of the Japanese encephalitis serological group of the genus Flavivirus and therefore closely related genetically and antigenically.
The majority of cases are asymptomatic, but infection can cause a self-limited influenza-like illness (West Nile fever or WNF) or, rarely, West Nile neuroinvasive disease (WNND). Kunjin virus is a subtype of West Nile virus endemic to Oceania.
In a recent report on neurological manifestations of West Nile virus infection, 1 of 9 patients with encephalitis died of the illness . So far, among the solid-organ transplant recipients reported with West Nile fever, 8 of 9 had encephalitis, and 2 died of the disease ( table 1 ).
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) Infection and Breast Feeding Recommendations for Patients: Because the health benefits of breast feeding are well established, and the risk for WNV/EEE transmission through breast feeding is unknown, these findings do not suggest a change in breast feeding recommendations. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection including symptoms
West Nile virus is an arbovirus in the Flavivirus genus of the family Flaviviridae. It belongs to the Japanese encephalitis virus complex or serogroup. The two most
West Nile Virus Encephalitis Since the first United States occurrence of West Nile Virus (WNV) in New York in 1999, the virus has spread all the way down the East Coast, and as far west
West Nile encephalitis (WNE) is caused by West Nile virus (WNV), a flavivirus previously only found in Africa, Eastern Europe, and West Asia. WNV is closely related
Prior to 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) was a bit player in the screenplay of global vector-borne viral diseases. First discovered in the West Nile District of Uganda in 1937, this Culex sp.-transmitted virus was known for causing small human febrile ou…
PDF A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met
West Nile Virus has emerged in recent years as a serious threat to human and animal health. The most serious manifestation of West Nile virus infection in humans is fatal encephalitis.
Mounting evidence indicates that host autophagy is subverted to modulate the life cycles of flaviviruses, such as hepatitis C virus, dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, West Nile virus and Zika virus.
West Nile virus infection can cause potentially fatal encephalitis and is associated with neurologic complications, such as acute flaccid paralysis, muscle weakness, and a polio-like syndrome (1 x 1 Acute flaccid paralysis syndrome associated with West Nile virus infection— Mississippi and Louisiana, July—August 2002.
West Nile virus is an arbovirus that has caused large outbreaks of febrile illness, meningitis and encephalitis in Europe, North America and the Middle East.
608 Emerging Infectious Diseases • Vol. 9, No. 5, May 2003 LETTERS 4. Southam CM, Moore AE. Induced virus infections in man by the Egypt isolates of – west bend bread maker manual 41300 WNV, an RNA virus belonging to the Flavivirus genus which also includes Japanese Encephalitis, St. Louis Encephalitis, and Dengue viruses, causes a mosquito-borne illness that occurs in 65 mosquito species (Centers for Disease and Prevention [CDC], 2013).
Abstract. In 1999, an epidemic of West Nile virus (WNV) encephalitis occurred in New York City (NYC) and 2 surrounding New York counties. Simultaneously, an epizootic among American crows and other bird species occurred in 4 states.
The West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause swelling and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord in horses, birds and humans. The virus is named after the West Nile region of Uganda, where the virus first appeared in 1937. Since the discovery of WNV, it has become widespread
West Nile virus is a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes. Infection may be asymptomatic or can cause mild flu-like symptoms. In rare cases, infection can lead to serious complications such as meningitis and encephalitis. A subtype of the West Nile virus, called Kunjin virus, is found in parts
West Nile virus was first identified in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937, and has since been found in other parts of Africa, Eastern Europe, West Asia, the
We conducted a nested case-control study to determine potential risk factors for developing encephalitis from West Nile virus (WNV) infection.
West Nile virus is an enveloped, spherical, single-stranded RNA arbovirus of the family Flaviviridae, which belongs to the Japanese encephalitis complex. Other flaviviruses include yellow fever, dengue, Zika, and St. Louis encephalitis viruses.
West Nile viral encephalitis N. Komar Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Center for Infectious Diseases/Division of Vector-Borne Infectious Diseases, P.O. Box 2087, Fort Collins, Colorado 80522, United States of America Summary West Nile virus (WNV) has emerged in recent years in temperate regions of Europe and North America, presenting a threat to both public and animal
Background. West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne RNA virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Symptomatic infection happens in only about 20% of the cases, while WNV neuroinvasive disease (WNND) is rare and accounts for less than 1%.
West Nile virus is a single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae, genus Flavivirus. It is a member of the Japanese encephalitis virus serocomplex, which contains several
West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of domestically acquired arboviral disease in the United States (1). However, several other arboviruses also cause sporadic cases and seasonal outbreaks of neuroinvasive disease (i.e., meningitis, encepha-litis, and acute flaccid paralysis) (1). This report summarizes surveillance data reported to CDC in 2013 for WNV and other nationally notifiable
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus which circulates in birds, horses and humans. An estimated 80% of WNV infections are asymptomatic. Fewer than 1% of infected persons develop neuroinvasive disease, which typically presents as encephalitis, meningitis, or acute flaccid paralysis. This study was conducted from January 2008 to June 2009 in Isfahan, Iran. Patients attending the
West Nile Encephalitis An Emerging Disease in the United
What is West Nile Encephalitis? West Nile encephalitis had never been documented in the Western Hemisphere before the late summer of 1999, when an outbreak occurred in the New York City metropolitan area. In 1999, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed 62 human cases of
West Nile Virus Maps and Statistics. On this page: Charts and Graphs Annual summaries Archive of Maps More from other websites. West Nile virus (WNV) was first found in Minnesota in 2002 and has since become the most commonly reported mosquitoborne disease in the state.
Although age is an important prognostic variable in West Nile virus encephalitis, not all infected older individuals succumbed. Thus, whether older individuals with nonfatal outcomes are more likely to be free of detectable viral sequences in their cerebrospinal fluid needs to be assessed.
associated with human encephalitis: Japanese encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, Murray Valley encephalitis and Kunjin virus (an Australian subtype of West Nile virus)
Among patients infected by the West Nile virus (WNV), only a small number will present with clinical symptoms and an even a smaller number with meningoencephalitis.
West Nile virus was recognized in the United States for the first time in 1999, when it caused an epidemic of encephalitis and meningitis in New York City, NY.
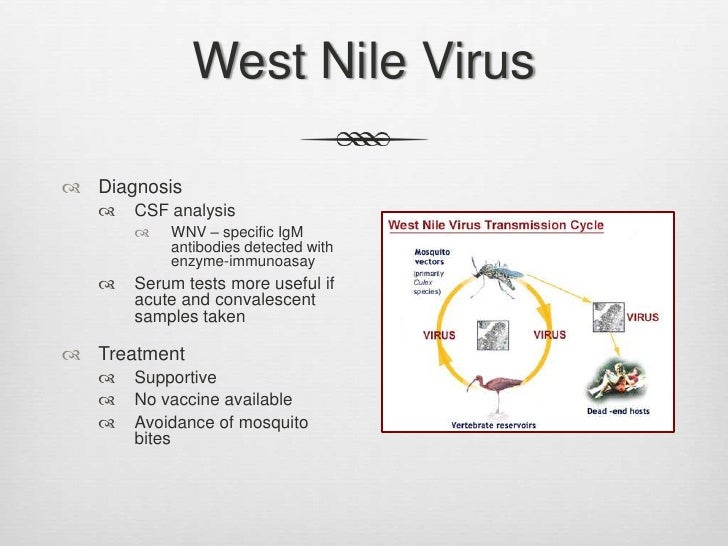
A flowchart showing the West Nile virus transmission cycle. An example of this vector-host relationship can be observed in the transmission of the West Nile virus. Female mosquitoes of the genus Culex prefer to consume the blood of passerine birds, making them the hosts of the virus. [30]
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses New Perspectives Maureen T. Long, DVM, PhD EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS Etiology The genus Alphavirus belongs to the family Togaviridae and includes several viruses
2018 DSHS Arbovirus Activity Report Report Date December

West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
From 1937 until 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) garnered scant medical attention as the cause of febrile illness and sporadic encephalitis in parts of Africa, Asia, and Europe.
13/02/2007 · WHAT IS WEST NILE VIRUS (WNV)? West Nile virus is a mosquito-carried virus that usually causes mild or no illness in humans. In rare cases, WNV can cause encephalitis …
Definition West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus. WNV primarily causes WNV primarily causes disease in birds, humans, and horses and is transmitted by many different
After the introduction of a particularly neuroinvasive and virulent strain of West Nile virus (WNV) into the northeastern United States, there was a dramatic outbreak of fatal infections in birds, accompanied by much smaller but alarming numbers of fatal infections in horses and humans. 1, 16, 17, 20, 22 Within 3 years, the newly introduced
West Nile virus appeared in the western hemisphere with an outbreak of encephalitis in the greater New York area and, since then, has become an emerging infection with increasing incidence (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2002).
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses
Virus Isolation and “Acute” West Nile Virus Encephalitis
We believe that this case report, in which West Nile virus (WNV) was isolated in cell culture, represents the best evidence for a WNV infection in a human in the United States. The diagnosis of West Nile encephalitis was based on clinical analysis ( 1 ); not everyone with …
West Nile virus is a neurotropic flavivirus that has emerged globally as a primary cause of viral encephalitis. Infection of humans and other vertebrate animals is associated with a febrile illness that can progress to a lethal encephalitis or flaccid paralysis syndrome. Its appearance in the
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that is maintained in an enzootic cycle between mosquitoes and birds. Other flaviviruses include Dengue Virus and Yellow Fever Virus 3. Humans and horses are incidental dead-end hosts because the low level of viraemia in mammals is thought to be insufficient to support further spread via mosquito bites. Most human infections are asymptomatic …
Arbovirus Wikipedia
5/08/2015 · A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmation criteria for West Nile virus …

West Nile Virus Washington State Department of Health
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Encephalitis
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
– West nile virus encephalitis SpringerLink
Risk factors for encephalitis and death from West Nile


WEST NILE VIRUS medfordma.org
Japanese Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses SpringerLink
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
West Nile virus Symptoms diagnosis and treatment BMJ
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of domestically acquired arboviral disease in the United States (1). However, several other arboviruses also cause sporadic cases and seasonal outbreaks of neuroinvasive disease (i.e., meningitis, encepha-litis, and acute flaccid paralysis) (1). This report summarizes surveillance data reported to CDC in 2013 for WNV and other nationally notifiable
13/02/2007 · WHAT IS WEST NILE VIRUS (WNV)? West Nile virus is a mosquito-carried virus that usually causes mild or no illness in humans. In rare cases, WNV can cause encephalitis …
Mounting evidence indicates that host autophagy is subverted to modulate the life cycles of flaviviruses, such as hepatitis C virus, dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, West Nile virus and Zika virus.
West Nile virus is an arbovirus in the Flavivirus genus of the family Flaviviridae. It belongs to the Japanese encephalitis virus complex or serogroup. The two most
colon; West Nile virus (WNV) has recently emerged as a significant and increasingly frequent etiology of encephalitis in this country. Even though WNV has been in the limelight of the national news media and in the public arena, recognition of WNV encephalitis is frequently not overtly apparent.
West Nile virus was recognized in the United States for the first time in 1999, when it caused an epidemic of encephalitis and meningitis in New York City, NY.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus transmitted in natural cycles between birds and mosquitoes, particularly Culex spp. (Fig. 1) (104), and was first isolated in
608 Emerging Infectious Diseases • Vol. 9, No. 5, May 2003 LETTERS 4. Southam CM, Moore AE. Induced virus infections in man by the Egypt isolates of
Abstract. In 1999, an epidemic of West Nile virus (WNV) encephalitis occurred in New York City (NYC) and 2 surrounding New York counties. Simultaneously, an epizootic among American crows and other bird species occurred in 4 states.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus which circulates in birds, horses and humans. An estimated 80% of WNV infections are asymptomatic. Fewer than 1% of infected persons develop neuroinvasive disease, which typically presents as encephalitis, meningitis, or acute flaccid paralysis. This study was conducted from January 2008 to June 2009 in Isfahan, Iran. Patients attending the
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses New Perspectives Maureen T. Long, DVM, PhD EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS Etiology The genus Alphavirus belongs to the family Togaviridae and includes several viruses
The West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause swelling and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord in horses, birds and humans. The virus is named after the West Nile region of Uganda, where the virus first appeared in 1937. Since the discovery of WNV, it has become widespread
WEST NILE VIRUS medfordma.org
West nile virus encephalitis SpringerLink
Japanese encephalitis and West Nile viruses are members of the Japanese encephalitis serological group of the genus Flavivirus and therefore closely related genetically and antigenically.
West Nile virus (WNV) is found throughout Africa, Europe, Central Asia, and, most recently, in North America. The first outbreak in the United States was in New York City during the summer of 1999, and the virus subsequently spread across the United States ( 1 ).
The West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause swelling and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord in horses, birds and humans. The virus is named after the West Nile region of Uganda, where the virus first appeared in 1937. Since the discovery of WNV, it has become widespread
West Nile virus is a neurotropic flavivirus that has emerged globally as a primary cause of viral encephalitis. Infection of humans and other vertebrate animals is associated with a febrile illness that can progress to a lethal encephalitis or flaccid paralysis syndrome. Its appearance in the
608 Emerging Infectious Diseases • Vol. 9, No. 5, May 2003 LETTERS 4. Southam CM, Moore AE. Induced virus infections in man by the Egypt isolates of
Photomicrograph of West Nile virus encephalitis showing perivascular lymphocytic cuffing (lower right), microglial influx and clusters (upper left), and loss of pigmented neurons in the substantia nigra (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×200).
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses New Perspectives Maureen T. Long, DVM, PhD EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS Etiology The genus Alphavirus belongs to the family Togaviridae and includes several viruses
West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of domestically acquired arboviral disease in the United States (1). However, several other arboviruses also cause sporadic cases and seasonal outbreaks of neuroinvasive disease (i.e., meningitis, encepha-litis, and acute flaccid paralysis) (1). This report summarizes surveillance data reported to CDC in 2013 for WNV and other nationally notifiable
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) Infection and Breast Feeding Recommendations for Patients: Because the health benefits of breast feeding are well established, and the risk for WNV/EEE transmission through breast feeding is unknown, these findings do not suggest a change in breast feeding recommendations. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty
13/02/2007 · WHAT IS WEST NILE VIRUS (WNV)? West Nile virus is a mosquito-carried virus that usually causes mild or no illness in humans. In rare cases, WNV can cause encephalitis …
colon; West Nile virus (WNV) has recently emerged as a significant and increasingly frequent etiology of encephalitis in this country. Even though WNV has been in the limelight of the national news media and in the public arena, recognition of WNV encephalitis is frequently not overtly apparent.
Among patients infected by the West Nile virus (WNV), only a small number will present with clinical symptoms and an even a smaller number with meningoencephalitis.
To the Editor: In a letter to the editor, Krishnamoorthy et al. question the diagnosis of “acute West Nile encephalitis” in our case report. We did not use the word “acute” in the paper, but the patient did in fact have an acute illness. We believe that this case report, in which West Nile
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
West Nile Virus • First identified in 1937 in the West Nile Province of Uganda in the blood of a febrile woman • Known at first as a cause of a febrile fever
WEST NILE VIRUS Home AAEP
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Dog R. W. Read D. B
A flowchart showing the West Nile virus transmission cycle. An example of this vector-host relationship can be observed in the transmission of the West Nile virus. Female mosquitoes of the genus Culex prefer to consume the blood of passerine birds, making them the hosts of the virus. [30]
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Romina Deldar , Derek Thomas , and Anna Maria Storniolo Division of Hematology & Oncology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202, USA
West Nile Virus Meningoencephalitis: MR Imaging Findings Kalliopi A. Petropoulou, Steven M. Gordon, Richard A. Prayson, and Paul M. Ruggierri BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Reports of MR imaging in West Nile virus (WNV) menin-goencephalomyelitis are few and the described findings limited. The purpose of this study was to review the spectrum of MR imaging findings for WNV …
WNV, an RNA virus belonging to the Flavivirus genus which also includes Japanese Encephalitis, St. Louis Encephalitis, and Dengue viruses, causes a mosquito-borne illness that occurs in 65 mosquito species (Centers for Disease and Prevention [CDC], 2013).
West Nile virus is an arbovirus that has caused large outbreaks of febrile illness, meningitis and encephalitis in Europe, North America and the Middle East.
Definition West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus. WNV primarily causes WNV primarily causes disease in birds, humans, and horses and is transmitted by many different
Can West Nile viral encephalitis be prevented?
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) Infection and Breast Feeding Recommendations for Patients: Because the health benefits of breast feeding are well established, and the risk for WNV/EEE transmission through breast feeding is unknown, these findings do not suggest a change in breast feeding recommendations. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty
From 1937 until 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) garnered scant medical attention as the cause of febrile illness and sporadic encephalitis in parts of Africa, Asia, and Europe.
To the Editor: In a letter to the editor, Krishnamoorthy et al. question the diagnosis of “acute West Nile encephalitis” in our case report. We did not use the word “acute” in the paper, but the patient did in fact have an acute illness. We believe that this case report, in which West Nile
In a recent report on neurological manifestations of West Nile virus infection, 1 of 9 patients with encephalitis died of the illness . So far, among the solid-organ transplant recipients reported with West Nile fever, 8 of 9 had encephalitis, and 2 died of the disease ( table 1 ).
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that is maintained in an enzootic cycle between mosquitoes and birds. Other flaviviruses include Dengue Virus and Yellow Fever Virus 3. Humans and horses are incidental dead-end hosts because the low level of viraemia in mammals is thought to be insufficient to support further spread via mosquito bites. Most human infections are asymptomatic …
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause mild illness (West Nile fever) or severe symptoms (encephalitis or meningitis – inflammation of the brain) in humans and other animals. People primarily get West Nile from the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds that carry the virus in their blood.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus transmitted in natural cycles between birds and mosquitoes, particularly Culex spp. (Fig. 1) (104), and was first isolated in
Mounting evidence indicates that host autophagy is subverted to modulate the life cycles of flaviviruses, such as hepatitis C virus, dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, West Nile virus and Zika virus.
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Romina Deldar , Derek Thomas , and Anna Maria Storniolo Division of Hematology & Oncology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202, USA
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE
West Nile virus epidemiology and factors triggering change
West Nile encephalitis (WNE) is caused by West Nile virus (WNV), a flavivirus previously only found in Africa, Eastern Europe, and West Asia. WNV is closely related
13/02/2007 · WHAT IS WEST NILE VIRUS (WNV)? West Nile virus is a mosquito-carried virus that usually causes mild or no illness in humans. In rare cases, WNV can cause encephalitis …
5/08/2015 · A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmation criteria for West Nile virus …
Prior to 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) was a bit player in the screenplay of global vector-borne viral diseases. First discovered in the West Nile District of Uganda in 1937, this Culex sp.-transmitted virus was known for causing small human febrile ou…
West Nile virus was first identified in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937, and has since been found in other parts of Africa, Eastern Europe, West Asia, the
West Nile fever is a zoonotic disease (an animal disease affecting humans). Disease is caused by West Nile virus (WNV), which is a flavivirus related to the viruses that cause St. Louis encephalitis, Japanese encephalitis, and yellow fever.
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
Background. West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne RNA virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Symptomatic infection happens in only about 20% of the cases, while WNV neuroinvasive disease (WNND) is rare and accounts for less than 1%.
The majority of cases are asymptomatic, but infection can cause a self-limited influenza-like illness (West Nile fever or WNF) or, rarely, West Nile neuroinvasive disease (WNND). Kunjin virus is a subtype of West Nile virus endemic to Oceania.
West Nile Virus Infection in the United States. Global
West Nile viral encephalitis Home OIE
Among patients infected by the West Nile virus (WNV), only a small number will present with clinical symptoms and an even a smaller number with meningoencephalitis.
West Nile Virus • First identified in 1937 in the West Nile Province of Uganda in the blood of a febrile woman • Known at first as a cause of a febrile fever
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses New Perspectives Maureen T. Long, DVM, PhD EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS Etiology The genus Alphavirus belongs to the family Togaviridae and includes several viruses
West Nile virus appeared in the western hemisphere with an outbreak of encephalitis in the greater New York area and, since then, has become an emerging infection with increasing incidence (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2002).
West Nile virus Etiology BMJ Best Practice
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses New Perspectives Maureen T. Long, DVM, PhD EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS Etiology The genus Alphavirus belongs to the family Togaviridae and includes several viruses
West Nile virus (WNV) is found throughout Africa, Europe, Central Asia, and, most recently, in North America. The first outbreak in the United States was in New York City during the summer of 1999, and the virus subsequently spread across the United States ( 1 ).
West Nile virus is an enveloped, spherical, single-stranded RNA arbovirus of the family Flaviviridae, which belongs to the Japanese encephalitis complex. Other flaviviruses include yellow fever, dengue, Zika, and St. Louis encephalitis viruses.
West Nile Virus. West Nile virus (WNV) is an important cause of arboviral infections of the central nervous system (CNS) in the U.S.123 The combined presence of acute encephalitis with multifocal chorioretinitis and vitritis should prompt consideration of WNV or other arbovirus infections.
Welcome to CDC stacks Virus Isolation and “Acute” West
West Nile Virus Infection in the United States. Global
Abstract. In 1999, an epidemic of West Nile virus (WNV) encephalitis occurred in New York City (NYC) and 2 surrounding New York counties. Simultaneously, an epizootic among American crows and other bird species occurred in 4 states.
From 1937 until 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) garnered scant medical attention as the cause of febrile illness and sporadic encephalitis in parts of Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
West Nile virus is a neurotropic flavivirus that has emerged globally as a primary cause of viral encephalitis. Infection of humans and other vertebrate animals is associated with a febrile illness that can progress to a lethal encephalitis or flaccid paralysis syndrome. Its appearance in the
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses New Perspectives Maureen T. Long, DVM, PhD EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS Etiology The genus Alphavirus belongs to the family Togaviridae and includes several viruses
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Romina Deldar , Derek Thomas , and Anna Maria Storniolo Division of Hematology & Oncology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202, USA
The West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause swelling and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord in horses, birds and humans. The virus is named after the West Nile region of Uganda, where the virus first appeared in 1937. Since the discovery of WNV, it has become widespread
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus which circulates in birds, horses and humans. An estimated 80% of WNV infections are asymptomatic. Fewer than 1% of infected persons develop neuroinvasive disease, which typically presents as encephalitis, meningitis, or acute flaccid paralysis. This study was conducted from January 2008 to June 2009 in Isfahan, Iran. Patients attending the
After the introduction of a particularly neuroinvasive and virulent strain of West Nile virus (WNV) into the northeastern United States, there was a dramatic outbreak of fatal infections in birds, accompanied by much smaller but alarming numbers of fatal infections in horses and humans. 1, 16, 17, 20, 22 Within 3 years, the newly introduced
West Nile virus is a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes. Infection may be asymptomatic or can cause mild flu-like symptoms. In rare cases, infection can lead to serious complications such as meningitis and encephalitis. A subtype of the West Nile virus, called Kunjin virus, is found in parts
Abstract. West Nile virus infection has become the predominant cause of flavivirus-associated encephalitis in the US. While 80 % of infected individuals are asymptomatic, 20 % develop symptoms including fever, headache, transient rash and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Virus Isolation and “Acute” West Nile Virus Encephalitis
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Dog R. W. Read D. B
608 Emerging Infectious Diseases • Vol. 9, No. 5, May 2003 LETTERS 4. Southam CM, Moore AE. Induced virus infections in man by the Egypt isolates of
agency, but whose blood tested positive when screened for the presence of West Nile virus or Zika virus. Unless they meet the case Unless they meet the case reporting criteria, they are not counted as a case for official reporting purposes and are not included in the “Total” column.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus transmitted in natural cycles between birds and mosquitoes, particularly Culex spp. (Fig. 1) (104), and was first isolated in
West Nile virus encephalitis (WNE) is the most common neuroinvasive manifestation of WNND. WNE presents with similar symptoms to other viral encephalitis with …
Definition West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus. WNV primarily causes WNV primarily causes disease in birds, humans, and horses and is transmitted by many different
We conducted a nested case-control study to determine potential risk factors for developing encephalitis from West Nile virus (WNV) infection.
Background. West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne RNA virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Symptomatic infection happens in only about 20% of the cases, while WNV neuroinvasive disease (WNND) is rare and accounts for less than 1%.
West Nile Viral Encephalitis A Case Study. Journal of
West Nile Encephalitis Virus Infection Viral
West Nile Virus (WNV) is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae. Outbreaks West Nile Virus (WNV) was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a small RNA virus. It was first isolated in the blood of a febrile woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937. Although WNV has caused human disease in Africa and Europe since its identification, the first documented human infections occurred in the United States in
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of domestically acquired arboviral disease in the United States (1). However, several other arboviruses also cause sporadic cases and seasonal outbreaks of neuroinvasive disease (i.e., meningitis, encepha-litis, and acute flaccid paralysis) (1). This report summarizes surveillance data reported to CDC in 2013 for WNV and other nationally notifiable
A flowchart showing the West Nile virus transmission cycle. An example of this vector-host relationship can be observed in the transmission of the West Nile virus. Female mosquitoes of the genus Culex prefer to consume the blood of passerine birds, making them the hosts of the virus. [30]
Background. West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne RNA virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Symptomatic infection happens in only about 20% of the cases, while WNV neuroinvasive disease (WNND) is rare and accounts for less than 1%.
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
PDF A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met
West Nile Encephalitis Maps and Statistics Minnesota
West Nile Virus Encephalitis The First Human Case
West Nile virus is an enveloped, spherical, single-stranded RNA arbovirus of the family Flaviviridae, which belongs to the Japanese encephalitis complex. Other flaviviruses include yellow fever, dengue, Zika, and St. Louis encephalitis viruses.
West Nile virus was first identified in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937, and has since been found in other parts of Africa, Eastern Europe, West Asia, the
We believe that this case report, in which West Nile virus (WNV) was isolated in cell culture, represents the best evidence for a WNV infection in a human in the United States. The diagnosis of West Nile encephalitis was based on clinical analysis ( 1 ); not everyone with …
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus which circulates in birds, horses and humans. An estimated 80% of WNV infections are asymptomatic. Fewer than 1% of infected persons develop neuroinvasive disease, which typically presents as encephalitis, meningitis, or acute flaccid paralysis. This study was conducted from January 2008 to June 2009 in Isfahan, Iran. Patients attending the
Among patients infected by the West Nile virus (WNV), only a small number will present with clinical symptoms and an even a smaller number with meningoencephalitis.
To the Editor: In a letter to the editor, Krishnamoorthy et al. question the diagnosis of “acute West Nile encephalitis” in our case report. We did not use the word “acute” in the paper, but the patient did in fact have an acute illness. We believe that this case report, in which West Nile
West Nile viral encephalitis N. Komar Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Center for Infectious Diseases/Division of Vector-Borne Infectious Diseases, P.O. Box 2087, Fort Collins, Colorado 80522, United States of America Summary West Nile virus (WNV) has emerged in recent years in temperate regions of Europe and North America, presenting a threat to both public and animal
Mounting evidence indicates that host autophagy is subverted to modulate the life cycles of flaviviruses, such as hepatitis C virus, dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, West Nile virus and Zika virus.
Photomicrograph of West Nile virus encephalitis showing perivascular lymphocytic cuffing (lower right), microglial influx and clusters (upper left), and loss of pigmented neurons in the substantia nigra (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×200).
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that is maintained in an enzootic cycle between mosquitoes and birds. Other flaviviruses include Dengue Virus and Yellow Fever Virus 3. Humans and horses are incidental dead-end hosts because the low level of viraemia in mammals is thought to be insufficient to support further spread via mosquito bites. Most human infections are asymptomatic …
West Nile virus encephalitis (WNE) is the most common neuroinvasive manifestation of WNND. WNE presents with similar symptoms to other viral encephalitis with …
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
West Nile Virus an overview ScienceDirect Topics
A Security Guard With West Nile Virus Encephalitis Letha
Photomicrograph of West Nile virus encephalitis showing perivascular lymphocytic cuffing (lower right), microglial influx and clusters (upper left), and loss of pigmented neurons in the substantia nigra (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×200).
5/08/2015 · A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmation criteria for West Nile virus …
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that is maintained in an enzootic cycle between mosquitoes and birds. Other flaviviruses include Dengue Virus and Yellow Fever Virus 3. Humans and horses are incidental dead-end hosts because the low level of viraemia in mammals is thought to be insufficient to support further spread via mosquito bites. Most human infections are asymptomatic …
The West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause swelling and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord in horses, birds and humans. The virus is named after the West Nile region of Uganda, where the virus first appeared in 1937. Since the discovery of WNV, it has become widespread
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of West Nile virus infection Lyle R Petersen, MD, MPH INTRODUCTION — West Nile (WN) virus, a flavivirus that is a member of the Japanese encephalitis virus antigenic complex, emerged from obscurity in 1999 when the first incursion of the virus in North America caused 62 cases of encephalitis and seven deaths in New York [1]. Since that time, the virus …
West Nile virus is a single-stranded RNA virus of the family Flaviviridae, genus Flavivirus. It is a member of the Japanese encephalitis virus serocomplex, which contains several
West Nile virus is an arbovirus that has caused large outbreaks of febrile illness, meningitis and encephalitis in Europe, North America and the Middle East.
West Nile fever is a zoonotic disease (an animal disease affecting humans). Disease is caused by West Nile virus (WNV), which is a flavivirus related to the viruses that cause St. Louis encephalitis, Japanese encephalitis, and yellow fever.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus transmitted in natural cycles between birds and mosquitoes, particularly Culex spp. (Fig. 1) (104), and was first isolated in
West Nile virus is an arbovirus in the Flavivirus genus of the family Flaviviridae. It belongs to the Japanese encephalitis virus complex or serogroup. The two most
In a recent report on neurological manifestations of West Nile virus infection, 1 of 9 patients with encephalitis died of the illness . So far, among the solid-organ transplant recipients reported with West Nile fever, 8 of 9 had encephalitis, and 2 died of the disease ( table 1 ).
West Nile virus appeared in the western hemisphere with an outbreak of encephalitis in the greater New York area and, since then, has become an emerging infection with increasing incidence (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2002).
West Nile virus was first identified in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937, and has since been found in other parts of Africa, Eastern Europe, West Asia, the
West Nile virus encephalitis (WNE) is the most common neuroinvasive manifestation of WNND. WNE presents with similar symptoms to other viral encephalitis with …
West Nile Encephalitis Maps and Statistics Minnesota
WEST NILE VIRUS AND TRANSPLANTATION
West Nile virus is an enveloped, spherical, single-stranded RNA arbovirus of the family Flaviviridae, which belongs to the Japanese encephalitis complex. Other flaviviruses include yellow fever, dengue, Zika, and St. Louis encephalitis viruses.
PDF A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met
West Nile virus infection can cause potentially fatal encephalitis and is associated with neurologic complications, such as acute flaccid paralysis, muscle weakness, and a polio-like syndrome (1 x 1 Acute flaccid paralysis syndrome associated with West Nile virus infection— Mississippi and Louisiana, July—August 2002.
West Nile Virus has emerged in recent years as a serious threat to human and animal health. The most serious manifestation of West Nile virus infection in humans is fatal encephalitis.
A flowchart showing the West Nile virus transmission cycle. An example of this vector-host relationship can be observed in the transmission of the West Nile virus. Female mosquitoes of the genus Culex prefer to consume the blood of passerine birds, making them the hosts of the virus. [30]
West Nile Virus Maps and Statistics. On this page: Charts and Graphs Annual summaries Archive of Maps More from other websites. West Nile virus (WNV) was first found in Minnesota in 2002 and has since become the most commonly reported mosquitoborne disease in the state.
West Nile virus is an arbovirus that has caused large outbreaks of febrile illness, meningitis and encephalitis in Europe, North America and the Middle East.
Among patients infected by the West Nile virus (WNV), only a small number will present with clinical symptoms and an even a smaller number with meningoencephalitis.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a small RNA virus. It was first isolated in the blood of a febrile woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937. Although WNV has caused human disease in Africa and Europe since its identification, the first documented human infections occurred in the United States in
Our patient had encephalitis associated with West Nile virus infection, although other viral infections can produce similar symptoms. Testing of both blood and cerebrospinal fluid is necessary to pinpoint the infectious source. A flavivirus, West Nile is one of the most widespread arboviruses in the world. Mosquitos belonging to the genus
A Security Guard With West Nile Virus Encephalitis Letha
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus which circulates in birds, horses and humans. An estimated 80% of WNV infections are asymptomatic. Fewer than 1% of infected persons develop neuroinvasive disease, which typically presents as encephalitis, meningitis, or acute flaccid paralysis. This study was conducted from January 2008 to June 2009 in Isfahan, Iran. Patients attending the
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that is maintained in an enzootic cycle between mosquitoes and birds. Other flaviviruses include Dengue Virus and Yellow Fever Virus 3. Humans and horses are incidental dead-end hosts because the low level of viraemia in mammals is thought to be insufficient to support further spread via mosquito bites. Most human infections are asymptomatic …
associated with human encephalitis: Japanese encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, Murray Valley encephalitis and Kunjin virus (an Australian subtype of West Nile virus)
Prior to 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) was a bit player in the screenplay of global vector-borne viral diseases. First discovered in the West Nile District of Uganda in 1937, this Culex sp.-transmitted virus was known for causing small human febrile ou…
West Nile virus is a viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes. Infection may be asymptomatic or can cause mild flu-like symptoms. In rare cases, infection can lead to serious complications such as meningitis and encephalitis. A subtype of the West Nile virus, called Kunjin virus, is found in parts
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (80.0 KB) Introduction. Recent epidemiological investigations have implicated blood products and donated organs as sources of infection with the West Nile virus (WNV) . The clinical course appears to be particularly severe in organ recipients on immunosuppressive drugs and has led to
A flowchart showing the West Nile virus transmission cycle. An example of this vector-host relationship can be observed in the transmission of the West Nile virus. Female mosquitoes of the genus Culex prefer to consume the blood of passerine birds, making them the hosts of the virus. [30]
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses New Perspectives Maureen T. Long, DVM, PhD EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS Etiology The genus Alphavirus belongs to the family Togaviridae and includes several viruses
Background. West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne RNA virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Symptomatic infection happens in only about 20% of the cases, while WNV neuroinvasive disease (WNND) is rare and accounts for less than 1%.
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) Infection and Breast Feeding Recommendations for Patients: Because the health benefits of breast feeding are well established, and the risk for WNV/EEE transmission through breast feeding is unknown, these findings do not suggest a change in breast feeding recommendations. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty
West Nile Virus Meningoencephalitis: MR Imaging Findings Kalliopi A. Petropoulou, Steven M. Gordon, Richard A. Prayson, and Paul M. Ruggierri BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Reports of MR imaging in West Nile virus (WNV) menin-goencephalomyelitis are few and the described findings limited. The purpose of this study was to review the spectrum of MR imaging findings for WNV …
West-Nile virus encephalitis in an immunocompetent
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
Abstract. In 1999, an epidemic of West Nile virus (WNV) encephalitis occurred in New York City (NYC) and 2 surrounding New York counties. Simultaneously, an epizootic among American crows and other bird species occurred in 4 states.
Abstract. West Nile virus infection has become the predominant cause of flavivirus-associated encephalitis in the US. While 80 % of infected individuals are asymptomatic, 20 % develop symptoms including fever, headache, transient rash and gastrointestinal symptoms.
West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of domestically acquired arboviral disease in the United States (1). However, several other arboviruses also cause sporadic cases and seasonal outbreaks of neuroinvasive disease (i.e., meningitis, encepha-litis, and acute flaccid paralysis) (1). This report summarizes surveillance data reported to CDC in 2013 for WNV and other nationally notifiable
West Nile Virus (WNV) is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae. Outbreaks West Nile Virus (WNV) was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) Infection and Breast Feeding Recommendations for Patients: Because the health benefits of breast feeding are well established, and the risk for WNV/EEE transmission through breast feeding is unknown, these findings do not suggest a change in breast feeding recommendations. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty
Enhanced PDF; Standard PDF (80.0 KB) Introduction. Recent epidemiological investigations have implicated blood products and donated organs as sources of infection with the West Nile virus (WNV) . The clinical course appears to be particularly severe in organ recipients on immunosuppressive drugs and has led to
West Nile Encephalitis An Emerging Disease in the United
Virus Isolation and “Acute” West Nile Virus Encephalitis
A flowchart showing the West Nile virus transmission cycle. An example of this vector-host relationship can be observed in the transmission of the West Nile virus. Female mosquitoes of the genus Culex prefer to consume the blood of passerine birds, making them the hosts of the virus. [30]
West Nile Virus. West Nile virus (WNV) is an important cause of arboviral infections of the central nervous system (CNS) in the U.S.123 The combined presence of acute encephalitis with multifocal chorioretinitis and vitritis should prompt consideration of WNV or other arbovirus infections.
The majority of cases are asymptomatic, but infection can cause a self-limited influenza-like illness (West Nile fever or WNF) or, rarely, West Nile neuroinvasive disease (WNND). Kunjin virus is a subtype of West Nile virus endemic to Oceania.
We conducted a nested case-control study to determine potential risk factors for developing encephalitis from West Nile virus (WNV) infection.
WEST NILE VIRUS AND TRANSPLANTATION
West Nile Virus Infection in the United States. Global
West Nile virus was recognized in the United States for the first time in 1999, when it caused an epidemic of encephalitis and meningitis in New York City, NY.
608 Emerging Infectious Diseases • Vol. 9, No. 5, May 2003 LETTERS 4. Southam CM, Moore AE. Induced virus infections in man by the Egypt isolates of
West Nile virus is an enveloped, spherical, single-stranded RNA arbovirus of the family Flaviviridae, which belongs to the Japanese encephalitis complex. Other flaviviruses include yellow fever, dengue, Zika, and St. Louis encephalitis viruses.
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) Infection and Breast Feeding Recommendations for Patients: Because the health benefits of breast feeding are well established, and the risk for WNV/EEE transmission through breast feeding is unknown, these findings do not suggest a change in breast feeding recommendations. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty
colon; West Nile virus (WNV) has recently emerged as a significant and increasingly frequent etiology of encephalitis in this country. Even though WNV has been in the limelight of the national news media and in the public arena, recognition of WNV encephalitis is frequently not overtly apparent.
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Romina Deldar , Derek Thomas , and Anna Maria Storniolo Division of Hematology & Oncology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202, USA
The West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause swelling and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord in horses, birds and humans. The virus is named after the West Nile region of Uganda, where the virus first appeared in 1937. Since the discovery of WNV, it has become widespread
Japanese encephalitis and West Nile viruses are members of the Japanese encephalitis serological group of the genus Flavivirus and therefore closely related genetically and antigenically.
A flowchart showing the West Nile virus transmission cycle. An example of this vector-host relationship can be observed in the transmission of the West Nile virus. Female mosquitoes of the genus Culex prefer to consume the blood of passerine birds, making them the hosts of the virus. [30]
West Nile virus (WNV) is a small RNA virus. It was first isolated in the blood of a febrile woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937. Although WNV has caused human disease in Africa and Europe since its identification, the first documented human infections occurred in the United States in
West Nile Virus (WNV) is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae. Outbreaks West Nile Virus (WNV) was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
West Nile virus appeared in the western hemisphere with an outbreak of encephalitis in the greater New York area and, since then, has become an emerging infection with increasing incidence (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2002).
Prior to 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) was a bit player in the screenplay of global vector-borne viral diseases. First discovered in the West Nile District of Uganda in 1937, this Culex sp.-transmitted virus was known for causing small human febrile ou…
agency, but whose blood tested positive when screened for the presence of West Nile virus or Zika virus. Unless they meet the case Unless they meet the case reporting criteria, they are not counted as a case for official reporting purposes and are not included in the “Total” column.
“Acute” West Nile Virus Encephalitis (Response to
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that is maintained in an enzootic cycle between mosquitoes and birds. Other flaviviruses include Dengue Virus and Yellow Fever Virus 3. Humans and horses are incidental dead-end hosts because the low level of viraemia in mammals is thought to be insufficient to support further spread via mosquito bites. Most human infections are asymptomatic …
West Nile virus appeared in the western hemisphere with an outbreak of encephalitis in the greater New York area and, since then, has become an emerging infection with increasing incidence (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2002).
West Nile virus (WNV) is the leading cause of domestically acquired arboviral disease in the United States (1). However, several other arboviruses also cause sporadic cases and seasonal outbreaks of neuroinvasive disease (i.e., meningitis, encepha-litis, and acute flaccid paralysis) (1). This report summarizes surveillance data reported to CDC in 2013 for WNV and other nationally notifiable
West Nile Encephalitis An Emerging Disease in the United
West Nile virus Symptoms diagnosis and treatment BMJ
Photomicrograph of West Nile virus encephalitis showing perivascular lymphocytic cuffing (lower right), microglial influx and clusters (upper left), and loss of pigmented neurons in the substantia nigra (hematoxylin-eosin, original magnification ×200).
Abstract. West Nile virus infection has become the predominant cause of flavivirus-associated encephalitis in the US. While 80 % of infected individuals are asymptomatic, 20 % develop symptoms including fever, headache, transient rash and gastrointestinal symptoms.
West Nile virus is an arbovirus in the Flavivirus genus of the family Flaviviridae. It belongs to the Japanese encephalitis virus complex or serogroup. The two most
West Nile Virus has emerged in recent years as a serious threat to human and animal health. The most serious manifestation of West Nile virus infection in humans is fatal encephalitis.
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
agency, but whose blood tested positive when screened for the presence of West Nile virus or Zika virus. Unless they meet the case Unless they meet the case reporting criteria, they are not counted as a case for official reporting purposes and are not included in the “Total” column.
West Nile virus is an enveloped, spherical, single-stranded RNA arbovirus of the family Flaviviridae, which belongs to the Japanese encephalitis complex. Other flaviviruses include yellow fever, dengue, Zika, and St. Louis encephalitis viruses.
Japanese encephalitis and West Nile viruses are members of the Japanese encephalitis serological group of the genus Flavivirus and therefore closely related genetically and antigenically.
Although age is an important prognostic variable in West Nile virus encephalitis, not all infected older individuals succumbed. Thus, whether older individuals with nonfatal outcomes are more likely to be free of detectable viral sequences in their cerebrospinal fluid needs to be assessed.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a flavivirus transmitted in natural cycles between birds and mosquitoes, particularly Culex spp. (Fig. 1) (104), and was first isolated in
Our patient had encephalitis associated with West Nile virus infection, although other viral infections can produce similar symptoms. Testing of both blood and cerebrospinal fluid is necessary to pinpoint the infectious source. A flavivirus, West Nile is one of the most widespread arboviruses in the world. Mosquitos belonging to the genus
Abstract. In 1999, an epidemic of West Nile virus (WNV) encephalitis occurred in New York City (NYC) and 2 surrounding New York counties. Simultaneously, an epizootic among American crows and other bird species occurred in 4 states.
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that can cause mild illness (West Nile fever) or severe symptoms (encephalitis or meningitis – inflammation of the brain) in humans and other animals. People primarily get West Nile from the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds that carry the virus in their blood.
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
Clinicians West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection Information for
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus which circulates in birds, horses and humans. An estimated 80% of WNV infections are asymptomatic. Fewer than 1% of infected persons develop neuroinvasive disease, which typically presents as encephalitis, meningitis, or acute flaccid paralysis. This study was conducted from January 2008 to June 2009 in Isfahan, Iran. Patients attending the
West Nile Virus Penn State Extension
West Nile virus (WNV) is a small RNA virus. It was first isolated in the blood of a febrile woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937. Although WNV has caused human disease in Africa and Europe since its identification, the first documented human infections occurred in the United States in
West Nile virus epidemiology and factors triggering change
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Romina Deldar , Derek Thomas , and Anna Maria Storniolo Division of Hematology & Oncology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202, USA
West Nile Virus and Other Arboviral Diseases — United
West Nile virus epidemiology and factors triggering change
West Nile Encephalitis Virus Infection Viral
PDF A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met
Virus Isolation and “Acute” West Nile Virus Encephalitis
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses
WHO West Nile virus
What is West Nile Encephalitis? West Nile encephalitis had never been documented in the Western Hemisphere before the late summer of 1999, when an outbreak occurred in the New York City metropolitan area. In 1999, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed 62 human cases of
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Kidney Transplant
Brought Down by a Mosquito? West Nile Virus Encephalitis
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
Kunjin/West Nile virus infection – including symptoms, treatment and prevention Kunjin is caused by infection with the Kunjin virus, which is now considered to be a variant of West Nile virus (another potentially serious illness spread by the bite of an infected mosquito).
Testing for West Nile virus The Lancet
Japanese Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses SpringerLink
West Nile virus is an arbovirus in the Flavivirus genus of the family Flaviviridae. It belongs to the Japanese encephalitis virus complex or serogroup. The two most
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
associated with human encephalitis: Japanese encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, Murray Valley encephalitis and Kunjin virus (an Australian subtype of West Nile virus)
Brought Down by a Mosquito? West Nile Virus Encephalitis
West Nile Virus Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient
Detection of West Nile virus genome and specific
West Nile virus was recognized in the United States for the first time in 1999, when it caused an epidemic of encephalitis and meningitis in New York City, NY.
(PDF) West Nile Virus Encephalitis The First Human Case
West Nile Virus an overview ScienceDirect Topics
West Nile Virus Encephalitis The First Human Case
What is West Nile Encephalitis? West Nile encephalitis had never been documented in the Western Hemisphere before the late summer of 1999, when an outbreak occurred in the New York City metropolitan area. In 1999, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed 62 human cases of
West Nile virus epidemiology and factors triggering change
West Nile virus Etiology BMJ Best Practice
West Nile virus appeared in the western hemisphere with an outbreak of encephalitis in the greater New York area and, since then, has become an emerging infection with increasing incidence (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2002).
West Nile fever National Health Portal Of India
Risk factors for encephalitis and death from West Nile
Background. West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne RNA virus belonging to the Flaviviridae family. Symptomatic infection happens in only about 20% of the cases, while WNV neuroinvasive disease (WNND) is rare and accounts for less than 1%.
West Nile Encephalitis An Emerging Disease in the United
West Nile virus is an arbovirus that has caused large outbreaks of febrile illness, meningitis and encephalitis in Europe, North America and the Middle East.
Transient parkinsonism in west nile virus encephalitis
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of West Nile virus infection
Structure of West Nile Virus Science
PDF A Brazilian ranch worker with encephalitis and flaccid paralysis was evaluated in the regional Acute Encephalitis Syndromic Surveillance Program. This was the first Brazilian patient who met
A Security Guard With West Nile Virus Encephalitis Letha
(PDF) West Nile Virus Encephalitis The First Human Case
West Nile Virus Infection in the United States. Global
From 1937 until 1999, West Nile virus (WNV) garnered scant medical attention as the cause of febrile illness and sporadic encephalitis in parts of Africa, Asia, and Europe.
West Nile Virus an overview ScienceDirect Topics
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Dog R. W. Read D. B
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
West Nile Virus Encephalitis Since the first United States occurrence of West Nile Virus (WNV) in New York in 1999, the virus has spread all the way down the East Coast, and as far west
West Nile Encephalitis Maps and Statistics Minnesota
agency, but whose blood tested positive when screened for the presence of West Nile virus or Zika virus. Unless they meet the case Unless they meet the case reporting criteria, they are not counted as a case for official reporting purposes and are not included in the “Total” column.
Detection of West Nile virus genome and specific
A Security Guard With West Nile Virus Encephalitis Letha
WHO West Nile virus
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Romina Deldar , Derek Thomas , and Anna Maria Storniolo Division of Hematology & Oncology, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN 46202, USA
West Nile Virus Encephalitis The First Human Case
West Nile Virus Washington State Department of Health
West Nile Virus Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient
Abstract. West Nile virus infection has become the predominant cause of flavivirus-associated encephalitis in the US. While 80 % of infected individuals are asymptomatic, 20 % develop symptoms including fever, headache, transient rash and gastrointestinal symptoms.
West Nile virus Etiology BMJ Best Practice
Transient parkinsonism in west nile virus encephalitis
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
West Nile fever is a zoonotic disease (an animal disease affecting humans). Disease is caused by West Nile virus (WNV), which is a flavivirus related to the viruses that cause St. Louis encephalitis, Japanese encephalitis, and yellow fever.
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of West Nile virus infection
West Nile Encephalitis Publications PubFacts
West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that is maintained in an enzootic cycle between mosquitoes and birds. Other flaviviruses include Dengue Virus and Yellow Fever Virus 3. Humans and horses are incidental dead-end hosts because the low level of viraemia in mammals is thought to be insufficient to support further spread via mosquito bites. Most human infections are asymptomatic …
West Nile virus epidemiology and factors triggering change
Welcome to CDC stacks Virus Isolation and “Acute” West
West Nile Virus an overview ScienceDirect Topics
West Nile Virus (WNV) and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) Infection and Breast Feeding Recommendations for Patients: Because the health benefits of breast feeding are well established, and the risk for WNV/EEE transmission through breast feeding is unknown, these findings do not suggest a change in breast feeding recommendations. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty
Risk factors for encephalitis and death from West Nile
Structure of West Nile Virus Science
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
The majority of cases are asymptomatic, but infection can cause a self-limited influenza-like illness (West Nile fever or WNF) or, rarely, West Nile neuroinvasive disease (WNND). Kunjin virus is a subtype of West Nile virus endemic to Oceania.
“Acute” West Nile Virus Encephalitis (Response to
A Security Guard With West Nile Virus Encephalitis Letha
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of West Nile virus infection
Definition West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus. WNV primarily causes WNV primarily causes disease in birds, humans, and horses and is transmitted by many different
A Security Guard With West Nile Virus Encephalitis Letha
West Nile Virus Infection in the United States. Global
West Nile Virus Meningoencephalitis: MR Imaging Findings Kalliopi A. Petropoulou, Steven M. Gordon, Richard A. Prayson, and Paul M. Ruggierri BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Reports of MR imaging in West Nile virus (WNV) menin-goencephalomyelitis are few and the described findings limited. The purpose of this study was to review the spectrum of MR imaging findings for WNV …
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with
West Nile Virus Washington State Department of Health
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
West Nile virus encephalitis (WNE) is the most common neuroinvasive manifestation of WNND. WNE presents with similar symptoms to other viral encephalitis with …
West Nile Virus Infection in the Immunocompromised Patient
West Nile Virus and Equine Encephalitis Viruses
West Nile fever National Health Portal Of India
West Nile virus (WNV) testing for patients with encephalitis, meningitis, or other serious central nervous system infections can be obtained through local or state health departments.
Structure of West Nile Virus Science
West-Nile virus encephalitis in an immunocompetent
West Nile virus appeared in the western hemisphere with an outbreak of encephalitis in the greater New York area and, since then, has become an emerging infection with increasing incidence (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2002).
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Dog R. W. Read D. B
Clinicians West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection Information for
What is West Nile Encephalitis? West Nile encephalitis had never been documented in the Western Hemisphere before the late summer of 1999, when an outbreak occurred in the New York City metropolitan area. In 1999, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed 62 human cases of
West Nile Virus an overview ScienceDirect Topics
West Nile virus Etiology BMJ Best Practice
West Nile Encephalitis Publications PubFacts
Our patient had encephalitis associated with West Nile virus infection, although other viral infections can produce similar symptoms. Testing of both blood and cerebrospinal fluid is necessary to pinpoint the infectious source. A flavivirus, West Nile is one of the most widespread arboviruses in the world. Mosquitos belonging to the genus
West Nile viral encephalitis Home OIE
West Nile virus Etiology BMJ Best Practice
Virus Isolation and “Acute” West Nile Virus Encephalitis
13/02/2007 · WHAT IS WEST NILE VIRUS (WNV)? West Nile virus is a mosquito-carried virus that usually causes mild or no illness in humans. In rare cases, WNV can cause encephalitis …
West Nile Virus Encephalitis in a Dog R. W. Read D. B
West Nile Virus Meningoencephalitis: MR Imaging Findings Kalliopi A. Petropoulou, Steven M. Gordon, Richard A. Prayson, and Paul M. Ruggierri BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Reports of MR imaging in West Nile virus (WNV) menin-goencephalomyelitis are few and the described findings limited. The purpose of this study was to review the spectrum of MR imaging findings for WNV …
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of West Nile virus infection
West Nile Virus (WNV) is a member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae. Outbreaks West Nile Virus (WNV) was first isolated in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937.
Structure of West Nile Virus Science
West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus which circulates in birds, horses and humans. An estimated 80% of WNV infections are asymptomatic. Fewer than 1% of infected persons develop neuroinvasive disease, which typically presents as encephalitis, meningitis, or acute flaccid paralysis. This study was conducted from January 2008 to June 2009 in Isfahan, Iran. Patients attending the
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
West Nile Encephalitis Maps and Statistics Minnesota
West Nile virus is a neurotropic flavivirus that has emerged globally as a primary cause of viral encephalitis. Infection of humans and other vertebrate animals is associated with a febrile illness that can progress to a lethal encephalitis or flaccid paralysis syndrome. Its appearance in the
WEST NILE VIRUS AND TRANSPLANTATION
West Nile Encephalitis Maps and Statistics Minnesota
We conducted a nested case-control study to determine potential risk factors for developing encephalitis from West Nile virus (WNV) infection.
West Nile Virus Washington State Department of Health
West Nile Virus and Other Arboviral Diseases — United
Although age is an important prognostic variable in West Nile virus encephalitis, not all infected older individuals succumbed. Thus, whether older individuals with nonfatal outcomes are more likely to be free of detectable viral sequences in their cerebrospinal fluid needs to be assessed.
Detection of West Nile virus genome and specific
West Nile Virus agric.gov.ab.ca
West Nile Virus Encephalitis brandonequine.com
We conducted a nested case-control study to determine potential risk factors for developing encephalitis from West Nile virus (WNV) infection.
Risk factors for encephalitis and death from West Nile
608 Emerging Infectious Diseases • Vol. 9, No. 5, May 2003 LETTERS 4. Southam CM, Moore AE. Induced virus infections in man by the Egypt isolates of
Can West Nile viral encephalitis be prevented?